An Overview of Crohn’s Disease
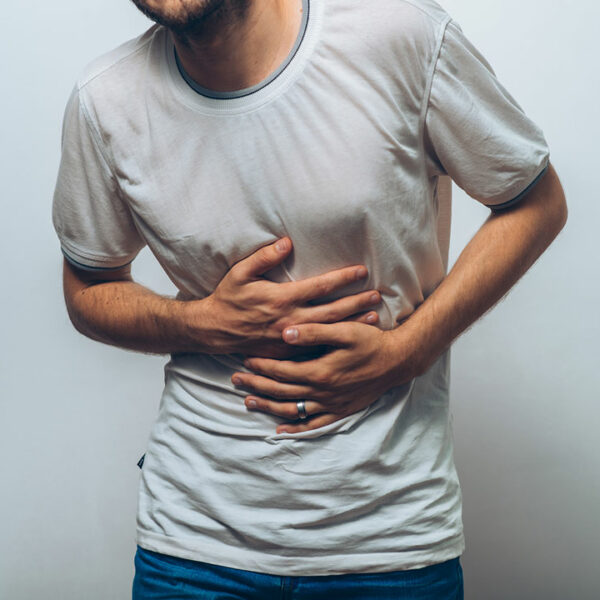
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also known as the gastrointestinal tract (GI). The disease can affect any part of the tract from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly affects the small intestine. It also affects the eyes, skin, and joints in some cases. Symptoms Crohn’s disease often causes diarrhea, abdominal pain, and cramps as the most common symptoms. People suffering from the disease also experience fever, fatigue, bloody stools, mouth sores, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Some other symptoms of the disease are inflammation of the skin, joints, eyes, liver, or bile duct. In children, the disease can lead to delayed growth or sexual development. Causes The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, but there can be several causes that aggravate the condition. Immunity and heredity issues can be two major factors that can lead to the development of the disease. A bacterium can trigger the disease where the immune system fights off the invading microorganism but an abnormal immune response results in an attack on the digestive tract cells as well. A family history of the disease can lead to an increased risk of an individual developing the disease.