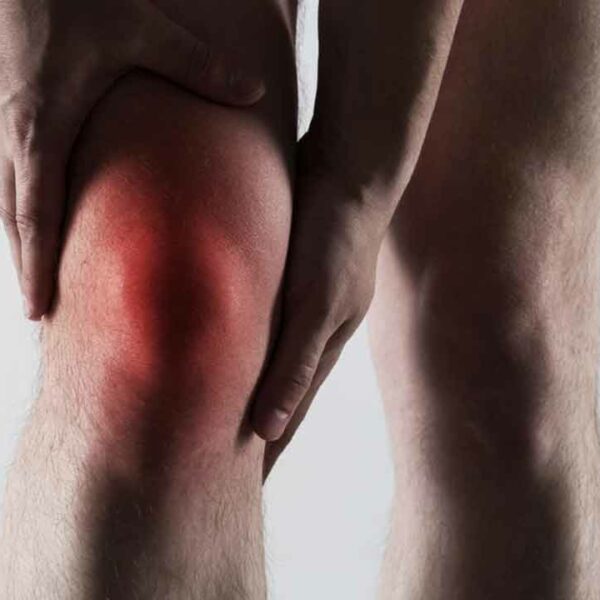
Gout: Its causes, diagnosis, and treatment
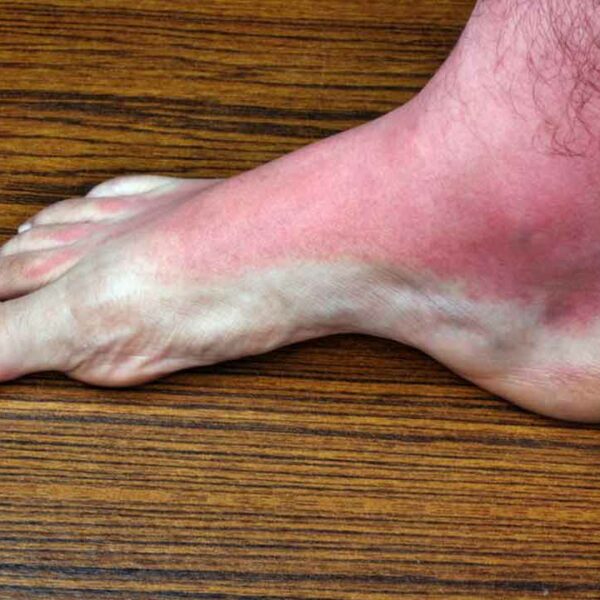
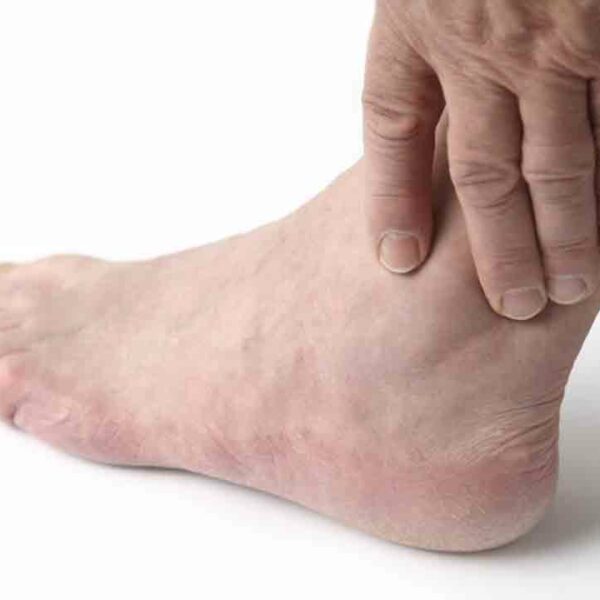
Gout is a type of arthritis which occurs when you have too much uric acid in your blood and it creates sharp crystals in one or more or your joints. Mostly it occurs in your big toe but it can also occur in your ankle, knee, wrist, foot, or elbow. Its attacks are sudden and cause severe pain and can be identified by redness and swelling around the joint. Generally, it lasts for 3 to 10 days, but the first 36 hours is extremely painful. After having the first attack, people usually don’t have another one for several months or years. Who are at risk? The ratio is 3:1 between men and women. It is quite common for men who are above 40 years of age. Women will have it mostly after their menopause. Those who are overweight and drink alcohol are at higher risk of suffering from gout. People who are having the following characteristics are more prone to having gout. Individuals with family history of having gout Taking certain diuretics for high blood pressure or other medications for psoriasis or rheumatoid arthritis. Those who have high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes or high cholesterol Those who have undergone gastric bypass surgery Causes of gout Your body produces uric acid to break down a chemical called purine.