Testing and Diagnosis of Asthma
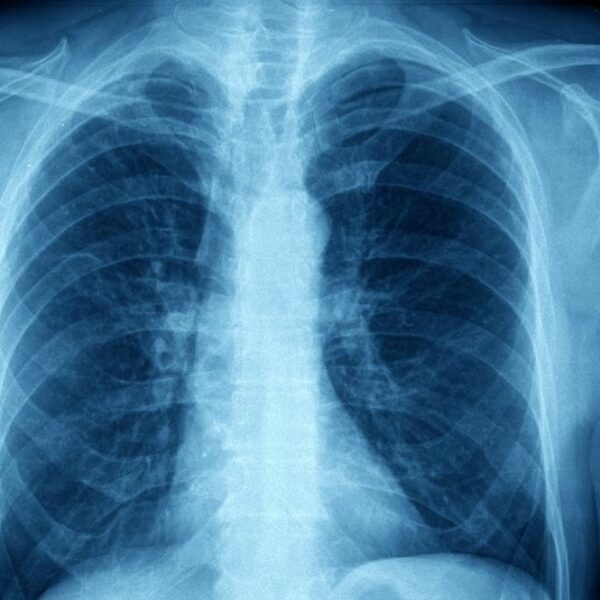
The following are some testing and diagnostic procedures that are used by doctors and medical providers to identify asthma cases. Spirometry The Spirometry test is used to diagnose asthma and identify its severity. In a spirometry test, you breathe forcefully into a tube and a device measures the amount of airflow passing through it. This is known as forced expiratory volume (FEV). It also measures your total lung capacity i.e. the largest amount of air you are able to breath out. This is known as Forced Vital Capacity (FVC). People will asthma will have restricted airflow, which will be represented by a decreased FEV and FEV:FVC ratio. If a patient is given medication to help open the lungs (bronchodilator) and then repeats the spirometry test, these numbers will show an improvement in most cases. [article_content_pin link=”http://www.health.online/medical-conditions/asthma-and-allergy/testing-and-diagnosis-of-asthma/” size=”small”] Peak Flow A peak flow meter can be used to monitor breathing capacity and to check the effectiveness of asthma treatments. This is a handheld device that you breathe into as hard as you can. As you blow an arrow will rise, indicating how much air you were able to breathe. The higher the number, the better. Most devices will also be color coded.