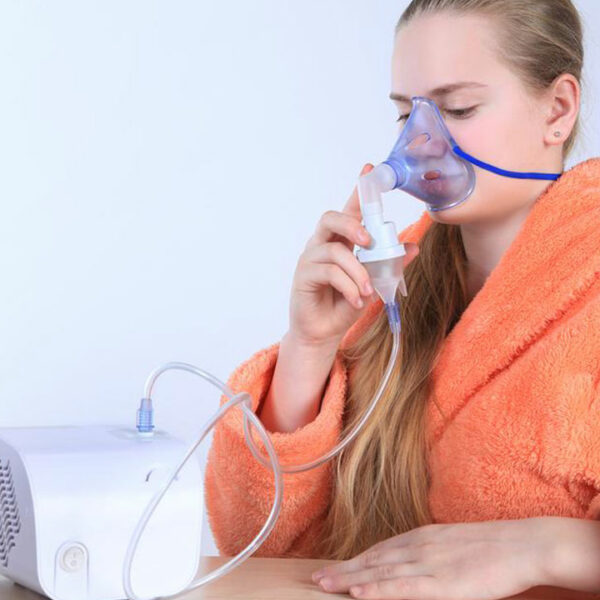
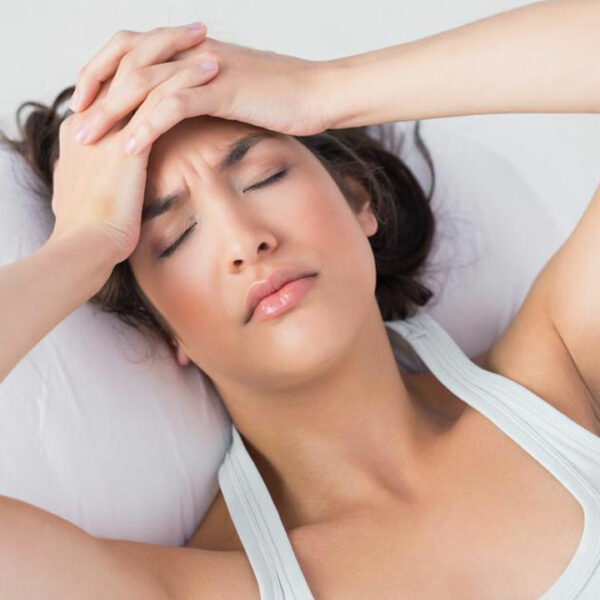
Chronic Bronchitis – Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Bronchitis can be defined as an irritation or inflammation of the airways, also known as bronchial tubes, in the lungs. These airways are the tubes through which the air passes. When these airways get inflamed, thick mucus forms in them. The mucus covers up the airways thus making it hard for the air to get into the lungs. Persistent coughing is an indication of bronchitis and produces mucus. The sputum plugs up the airways and causes difficulty in breathing, resulting in a feeling of tightness in the chest. In this article, the symptoms along with effective treatment for chronic bronchitis have been outlined. Chronic means that the problem or condition lasts a long time ranging from a few days to several months. Chronic bronchitis is bronchitis that usually lasts more than 3 months and often occurs with emphysema. The combination of these disease causes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Symptoms of chronic bronchitis The most common symptoms of acute bronchitis: Sore throat Fever constant coughing accompanied by yellow or green mucus Chest congestion Shortness of breath Wheezing Chills Body aches Causes of chronic bronchitis Viruses are often blamed for causing chronic bronchitis. Viruses attack the coating of the bronchial tree and cause inflammation. The same viruses that are responsible for causing colds can also cause acute bronchitis.