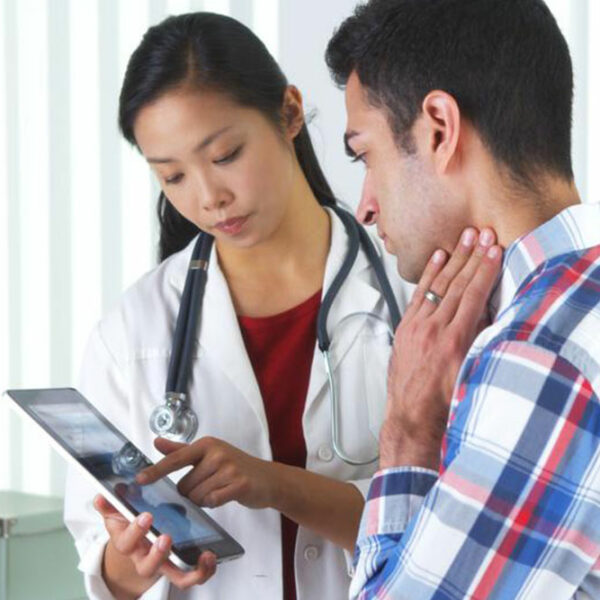
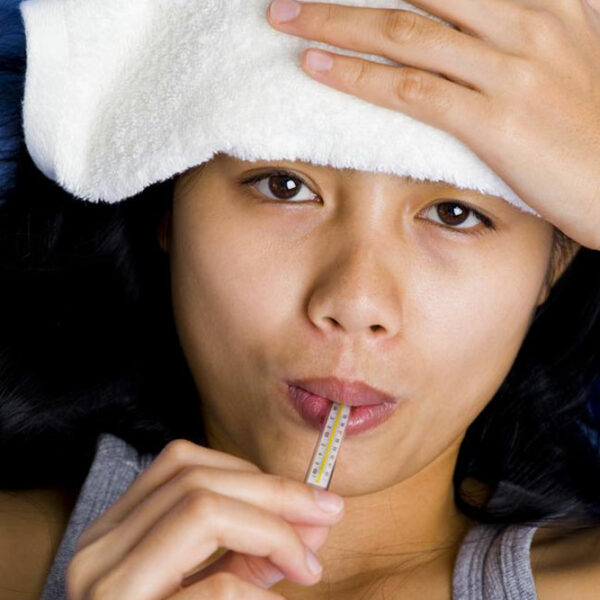
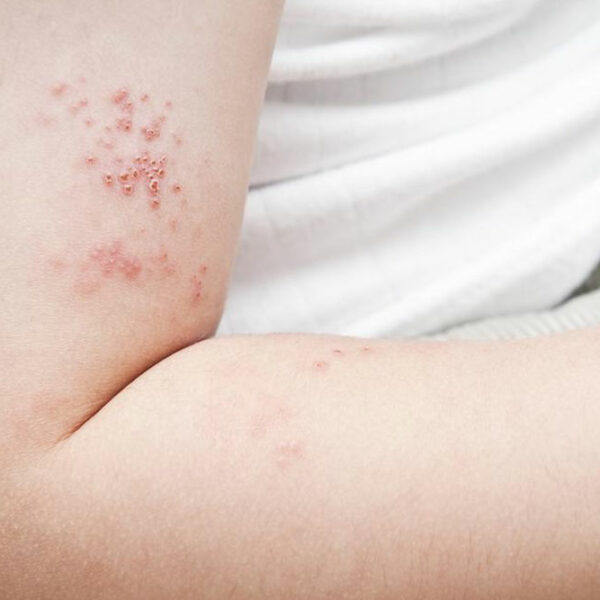
Stages of HIV infection
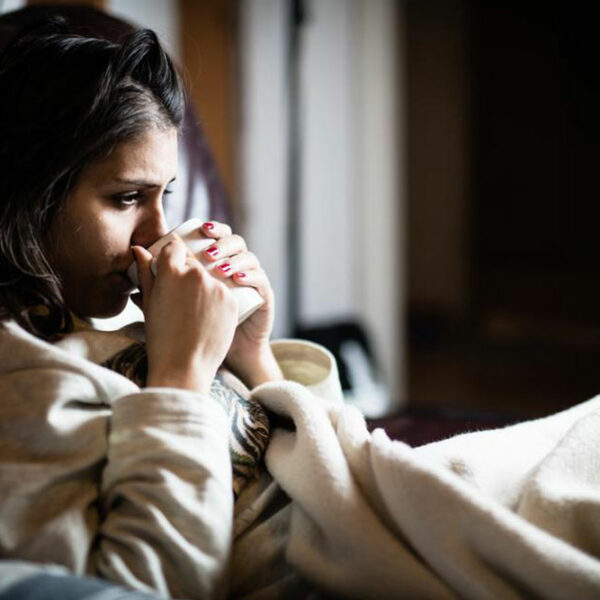
HIV or Human Immuno-Deficiency Virus is a life-threatening virus that attacks the CD-4 lymphocytes of the human body and brings down its immune system to a level that it is vulnerable to all kinds of diseases. If not treated timely, the infected person dies due to the direct effect of all other diseases rather than HIV alone. HIV has three stages; Acute HIV infection When HIV virus enters the blood stream of the body, it immediately attacks the lymphocytes in the blood. The patient may not notice its effect in the initial weeks until the time when the lymphocytes count in the blood stream has reduced to a drastic level. Flu like symptoms would begin to a appear. High fever with head ache and nausea would be persistent for a couple of days. Some people might even experience Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. These symptoms would remain for a normal period and the patient would return to normal state without ever knowing the real cause of the flu infection. The second stage is called as the chronic infection stage . The patient enters this stage when the HIV starts killing off CD-4 cells thereby weakening the immune system on a daily basis.