An Overview Of Cellulitis
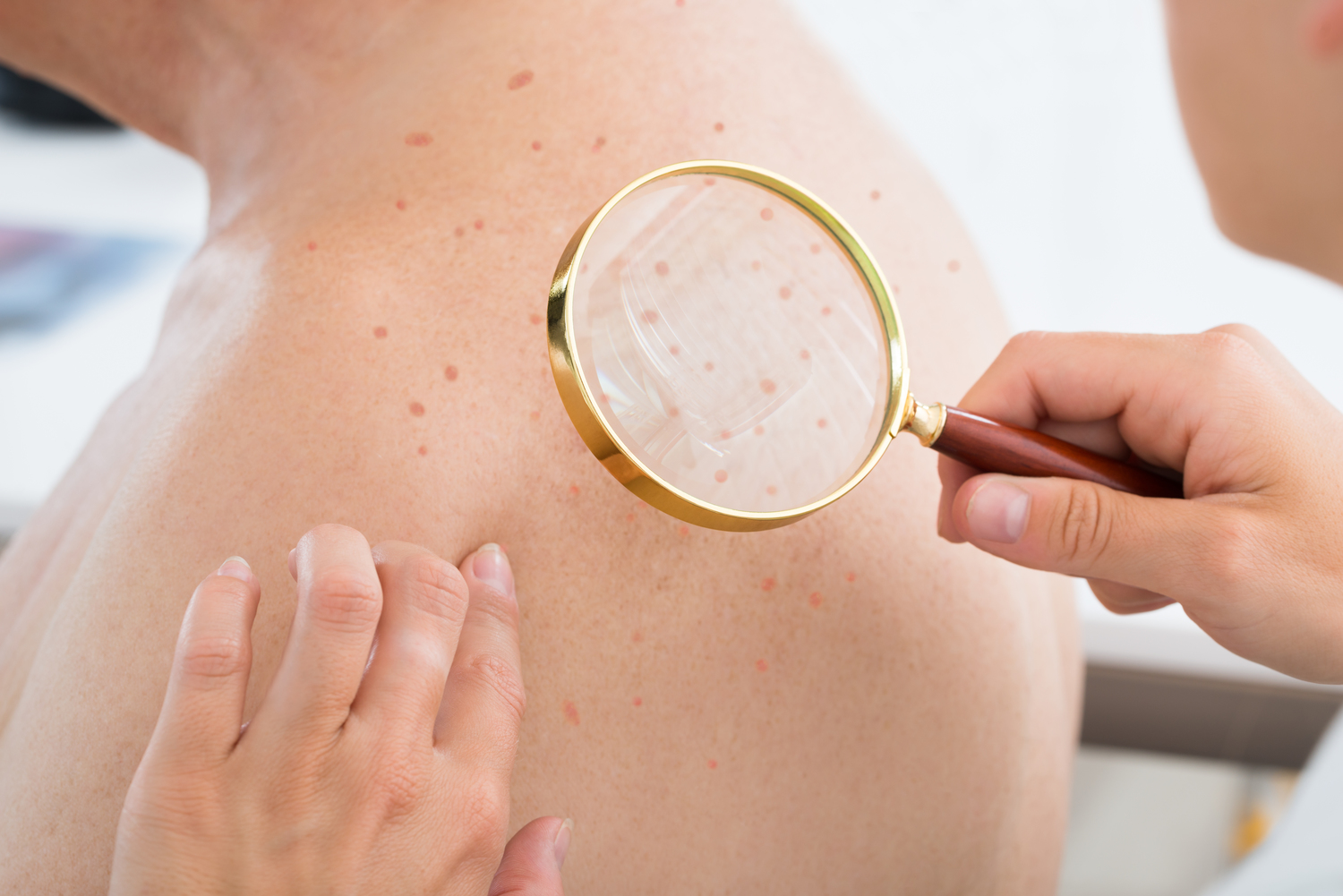
An overview of cellulitis
Cellulitis is a painful skin condition wherein red angry patches appear on the skin of the legs. It is a bacterial skin infection and may appear even on the hands or other parts of the body. It should be treated immediately as it may spread to the underlying tissues, and, in some severe cases, to the bloodstream or the lymph nodes. The swollen area might be painful to touch. People with eczema or psoriasis have a greater chance of developing cellulitis.
What causes cellulitis and why does it occur?
- Cellulitis is often caused by several types of bacteria, most notably by the staphylococcus as well as the streptococcus bacteria. It is not uncommon to notice a cut or insect bite on the swollen area.
- The bacteria enter through a cut or a crack in the skin. Sometimes, even surgical incisions are the reason for the entry of bacteria; so you should take great care.
- Some other cellulitis causes could be a weakened immune system, eczema, or athlete’s foot. Diabetes and extensive use of intravenous drugs are also responsible for cellulitis.
What are the symptoms of cellulitis?
- The symptoms in the initial stages are varied and include painful red patches on the skin, the skin developing a tight and glossy appearance, an abscess that has pus formed within, pain and inflammation in the area, tenderness, a rash that spreads quickly, or fever.
- A more serious condition could entail tiredness, dizziness, chills, shaking, lethargy, fever, muscle aches, and extensive sweating. Patients are advised to visit a doctor as soon as any of these symptoms appear so as to avoid any unnecessary discomfort.
- Red streaks, blisters, fatigue, and feeling light-headed or drowsy could mean that cellulitis is spreading and you should take immediate action by visiting a doctor and undertaking treatment.
What are some possible complications that could arise due to cellulitis?
- If cellulitis enters the bloodstream or if the doctors suspect that it has infected the lymph nodes, things may take a turn for the worse. In some cases, the infection could enter the deep layers of the tissue.
- Some of the possible complications that could arise are a bone infection, a blood infection, gangrene, or an inflammation of the lymph vessels.
How is cellulitis treated?
- Most doctors prescribe a 10-21-day regimen of oral antibiotics that is likely to address the situation, and you will begin to see results in a week. However, it is important to continue the course in order to get rid of the infection.
- Pain relievers may also be prescribed, and doctors suggest keeping the affected limb elevated to help with blood flow. The medication should work fast unless the condition is chronic or there is something wrong with the patient’s immune system.
- Hospitalization is rare, but it is advised if there is a preexisting condition or the patient needs to be under observation. A high blood pressure, a high temperature, no response to antibiotics, or a weakened immune system could be some reasons for why hospitalization is needed.
How can the occurrence of cellulitis be prevented?
- There are certain measures that you may take to avoid infection like cleaning a cut or wound with an antibiotic ointment daily.
- Alternatively, you should apply a bandage to any wound until a scab forms and watch out for redness, swelling, or formation of pus. Some people may have preexisting conditions, and they need to take more care.
- If you are prone to skin conditions, ensure that you keep the skin moist in order to prevent cracking. Promptly address athlete’s foot to take care of skin infection. You should wear protective equipment while working or playing contact sports.
These directions should be closely followed, and people are advised to monitor their feet for any sign of injury, a cut, or a wound. If you take ample care, you may avoid cellulitis causes from affecting you, thereby staying away from antibiotics and a visit to the doctor.



